Chalazion
A chalazion is a swelling in the eyelid caused by inflammation of one of the small oil-producing glands located in the upper and lower eyelids. A chalazion is sometimes confused with a hordeolum (stye), which also appears as a lump in the eyelid. Both occur in the small glands inside the eyelid. A stye is a bacterial infection (usually Staphylococcus that normally live on the skin) and forms a red, sore lump. Chalazions are inflammatory and tend to occur farther from the edge of the eyelid than styes and tend to “point” toward the inside of the eyelid. Sometimes a chalazion can cause the entire eyelid to swell suddenly, but usually there is a particular tender point.
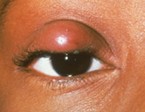
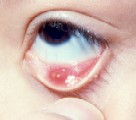
When a chalazion is small and without symptoms, it may disappear on its own. If the chalazion is large, it may cause blurred vision. Chalazions are treated with any or a combination of the following methods:
- Warm compresses help to clear the clogged gland. Take a clean washcloth and run hot water over it. Place over the affected area for 10-15 minutes (you need to re-warm the washcloth several times during this period) three to four times daily. Most chalazia will drain spontaneously with the help of warm compresses.
- Antibiotic ointments may be prescribed if bacteria infect the chalazion
- Steroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation.
- Surgery may be used to drain a large chalazion if it does not respond to other treatments. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia the office.
Chalazions usually respond well to treatment, although some people are prone to recurrences. If a chalazion recurs in the same place, your ophthalmologist may suggest a biopsy to rule out problems that are more serious.
